In London, strict compliance with emergency lighting regulations is not only a legal obligation but a vital aspect of ensuring public safety in commercial settings. Governed by the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005, these regulations require all premises to have sufficient emergency lighting to support safe evacuation during emergencies. This guide serves as an invaluable resource for understanding these requirements, detailing the types of systems, installation protocols, and maintenance necessities. However, beyond the technical specifications and legal stipulations, one must consider the real-world applications and challenges these regulations present to business owners and safety officers. What are the practical implications of these regulations on the daily operations of a business, and how do real-life scenarios compare to the ideals outlined in the regulatory framework, Let’s understand the Comprehensive Guide to Emergency Lighting Regulations in London.
Understanding Emergency Lighting
Understanding emergency lighting is crucial for ensuring the safety and compliance of any building during a power outage. The foundation of effective emergency lighting design hinges on integrating technological advancements to create systems that are not only compliant but also efficient and reliable under emergency conditions.
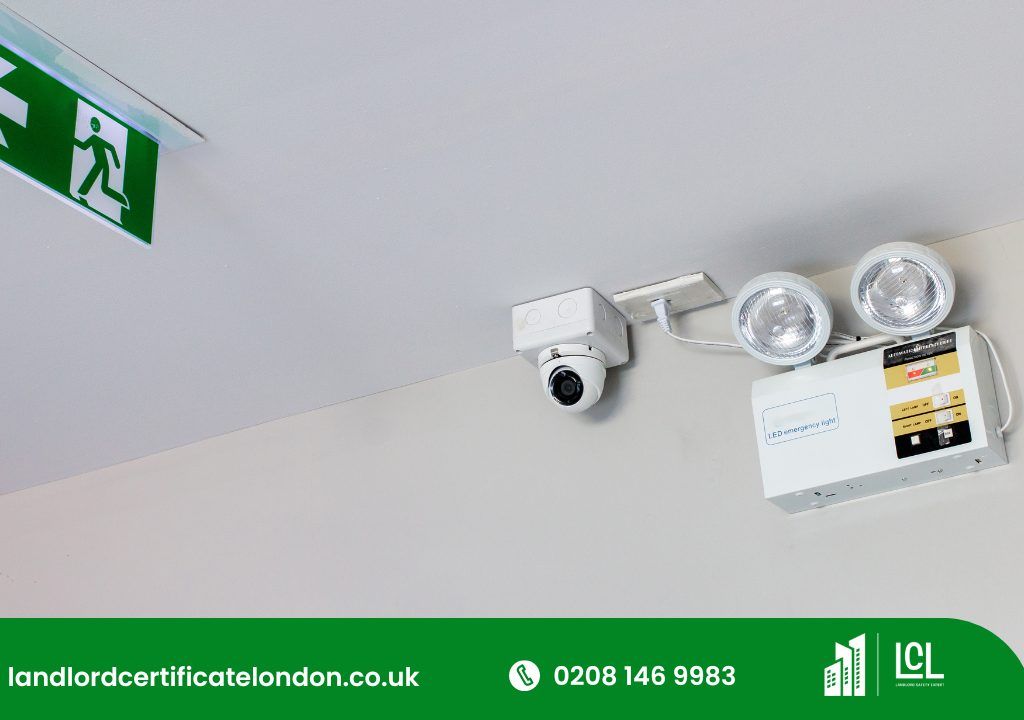

Innovations in lighting technology have significantly influenced the evolution of emergency lighting solutions, leading to the development of more durable, energy-efficient, and smarter lighting systems. These systems are now equipped with self-diagnostic features that enable real-time monitoring and maintenance alerts, thereby reducing the likelihood of failures during critical periods.
Additionally, advancements in LED technology have been pivotal, as they offer longer lifespans, better energy efficiency, and improved luminance compared to traditional lighting solutions. The design process has become more sophisticated with software and modeling tools that allow for precise placement and intensity calculations, ensuring that emergency lighting is both effective and minimally intrusive.
This meticulous approach to emergency lighting design not only enhances safety but also ensures that the lighting systems integrate seamlessly with the aesthetic and functional aspects of the building environment, maintaining the balance between safety and design integrity.
Legal Requirements
Navigating the legal landscape governing emergency lighting is crucial for compliance and building safety. In London, the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 serves as the foundational legal framework, mandating the installation and maintenance of emergency lighting systems in all commercial premises. This includes buildings occupied by the public, such as hotels, schools, hospitals, and office spaces.
Compliance with British Standard 5266 and the European Standard BS EN 1838 specifies the minimum requirements for the placement, operation, and efficacy of emergency lighting fixtures to ensure optimal fire safety and emergency preparedness.
For building owners and facilities managers, adherence to these standards is not merely a regulatory formality but a critical component of occupant safety. Emergency lighting systems must be designed to illuminate escape routes effectively and ensure that fire safety signs are distinctly visible during emergencies, thereby minimizing panic and confusion.
Furthermore, the law requires regular testing and maintenance of these systems; failure to comply can lead to severe legal repercussions, including fines and prosecution. Compliance ensures that in the event of a power outage or fire, the environment remains navigable, substantially mitigating the risks associated with emergency evacuations.
Key Functions
Building on the legal framework outlined previously, we now examine the key functions of emergency lighting, which play a pivotal role in ensuring safety during unforeseen power outages and emergencies.
Primarily, emergency lighting benefits users by illuminating escape routes, thereby facilitating safe and orderly evacuation. This is crucial not only for aiding occupants in exiting the building but also for assisting rescue and emergency services to perform their duties effectively.
The design and implementation of emergency lighting systems are closely integrated with evacuation planning. Strategic placement of lighting ensures that all exit paths and obstacles are visible, reducing panic and potential injuries during evacuations.
This planning must consider various scenarios and accommodate all building zones to maintain high safety standards.
Furthermore, emergency lighting supports essential visibility in emergencies, ensuring that critical tasks can be completed safely. It also helps prevent total darkness, a key factor that can lead to chaos and confusion.
The technical requirements for these systems are stringent, ensuring that lighting remains operational for a minimum duration, typically between one to three hours, which is vital for the completion of safe evacuation processes.
This duration is meticulously calculated based on building size, complexity, and the maximum expected occupancy.
Types of Systems
Emergency lighting systems are categorized into several types, each designed to meet specific requirements and scenarios within a building’s safety protocols.
These systems include maintained, non-maintained, and combined emergency lighting, each leveraging advanced battery technology to enhance system efficiency and reliability during critical situations.
Maintained emergency lighting operates continuously, using the same luminaires for both normal and emergency operations. This system is particularly beneficial in places where constant illumination is crucial, such as hospitals and cinemas.
Here, the emphasis on battery technology ensures that the lights remain operational for a minimum mandated period, typically between 1 to 3 hours, during a power outage.
Non-maintained emergency lighting, on the other hand, remains inactive until a power failure occurs. This type is often installed in escape routes and areas not in regular use, such as stairwells.
The efficiency of this system lies in its ability to conserve energy and battery life, activating only when necessary.
Combined emergency lighting systems integrate features of both maintained and non-maintained systems. They provide continuous illumination and are equipped with robust battery solutions to support prolonged emergency operations.
This dual functionality not only enhances safety but also optimizes operational readiness and response during emergencies.
Installation Guidelines
Understanding the various types of emergency lighting systems sets the stage for implementing effective installation practices. Mastery of installation guidelines is crucial, as each emergency lighting system presents unique challenges and requires specific installation techniques to ensure operational efficacy during crises.

Installation challenges often arise from the architectural complexities of buildings. For instance, the integration of escape route lighting in older structures demands meticulous planning to navigate historical preservation concerns while ensuring compliance with the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 and BS 5266 standards. Achieving this balance requires a deep understanding of both the physical and regulatory landscapes.
To overcome these challenges, adherence to installation best practices is paramount. This involves conducting thorough risk assessments to identify critical areas needing illumination, such as stairwells and changes in floor levels.
Professional installers should utilize only certified equipment that meets UK standards for emergency lighting. Furthermore, strategic placement of fixtures is essential, ensuring that illumination is both effective and minimally invasive to the building’s aesthetic.
Effective installation also hinges on collaboration with certified electrical engineers who can address the specific power supply considerations for maintained and non-maintained systems, ensuring that emergency lights activate reliably during power failures.
Maintenance Protocols
Maintaining emergency lighting systems is crucial for ensuring their reliability and effectiveness during critical situations. Effective maintenance protocols are essential to uphold the operational integrity of these systems, especially focusing on areas like emergency signage and battery longevity. Scheduled maintenance not only ensures compliance with regulations but also enhances the safety of building occupants by guaranteeing that all components function optimally when needed.
| Maintenance Aspect | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Emergency Signage | Regular checks for visibility and correct operation. |
| Battery Longevity | Assessment and replacement to prevent failures. |
| General System Health | Comprehensive system tests excluding specific testing procedures. |
Professionals involved in the maintenance of emergency lighting must possess a deep understanding of system components and their operational thresholds. This includes knowledge of battery types used in emergency lighting, their charge cycles, and expected lifespans. Regular reviews and replacements of batteries are critical to prevent sudden failures during emergencies. Additionally, emergency signage must be inspected for clarity and functionality, ensuring that it remains visible and legible even in adverse conditions. This holistic approach to maintenance safeguards the continuous readiness and effectiveness of emergency lighting systems.
Testing Procedures
Initiating robust testing procedures is essential for the integrity and reliability of emergency lighting systems. These systems, pivotal in emergency preparedness, rely on cutting-edge lighting technology to function under adverse conditions.

To ensure their operational efficacy, rigorous testing protocols must be adopted, as outlined in BS EN 50172 and BS 5266-8. Monthly functional tests involve simulating a power failure to activate the emergency lighting, allowing for verification that all units are operational and illuminate the required areas effectively.
Annually, a full-rated duration test is mandatory, wherein emergency lights must remain operational for the full duration stipulated by their design specifications—typically three hours. This stringent testing not only confirms battery health and light functionality over extended periods but also identifies any degradation in light intensity, which could compromise safety.
Technicians carrying out these tests need to meticulously document all findings, from operational readiness to any faults. This documentation is crucial for maintaining compliance records and facilitating any necessary repairs or replacements to ensure that the emergency lighting system remains a reliable part of the building’s safety infrastructure.
Compliance and Penalties
Compliance with emergency lighting regulations is not merely a recommendation but a stringent requirement enforced by law. In London, adherence to the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005, along with standards such as BS 5266 and BS EN 1838, is compulsory.
Regulatory enforcement agencies, including local fire brigades and building control officers, are tasked with ensuring these standards are met through routine inspections and audits.
Non-compliance consequences are severe, reflecting the critical nature of emergency lighting in ensuring occupant safety during emergencies. Penalties can range from hefty fines to criminal charges, depending on the severity and the risk posed by non-compliance.
Additionally, failure to adhere to these regulations can lead to mandatory shutdown of facilities that do not meet the legal requirements, further emphasizing the importance of compliance.
Building owners and managers must ensure that emergency lighting systems are not only installed but also meticulously maintained and regularly tested.
Documentation of these tests and maintenance activities must be kept as they can be requested by regulatory bodies at any time. This rigorous approach helps mitigate risks, ensuring that all occupants have safe passage in the event of an emergency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, adherence to the emergency lighting regulations as outlined in the Comprehensive Guide is imperative for ensuring occupant safety and legal compliance in London’s commercial premises. Meticulous installation, rigorous maintenance, and consistent testing of emergency lighting systems are crucial. Failing to comply not only risks severe legal penalties but also compromises the safety of individuals during emergencies. Therefore, thorough understanding and implementation of these guidelines are essential for all stakeholders.
Visit our website for More Safety Services.
About the Author: LandlordCertificate
Related Posts
Get Social
Recent Posts
- How Portable Electric Appliances Make Life Easier and More Efficient
- Do You Need a Fire Door Test Certificate? Legal and Safety Insights
- EPC Certificate London: Ensuring Compliance for Residential and Commercial Buildings
- London Gas Safety Certificate: Everything Landlords Need to Know
- Fire Alarm Inspection London: How to Replace and Update Your System